- 2.04 MB
- 2022-06-16 12:29:31 发布
- 1、本文档共5页,可阅读全部内容。
- 2、本文档内容版权归属内容提供方,所产生的收益全部归内容提供方所有。如果您对本文有版权争议,可选择认领,认领后既往收益都归您。
- 3、本文档由用户上传,本站不保证质量和数量令人满意,可能有诸多瑕疵,付费之前,请仔细先通过免费阅读内容等途径辨别内容交易风险。如存在严重挂羊头卖狗肉之情形,可联系本站下载客服投诉处理。
- 文档侵权举报电话:19940600175。
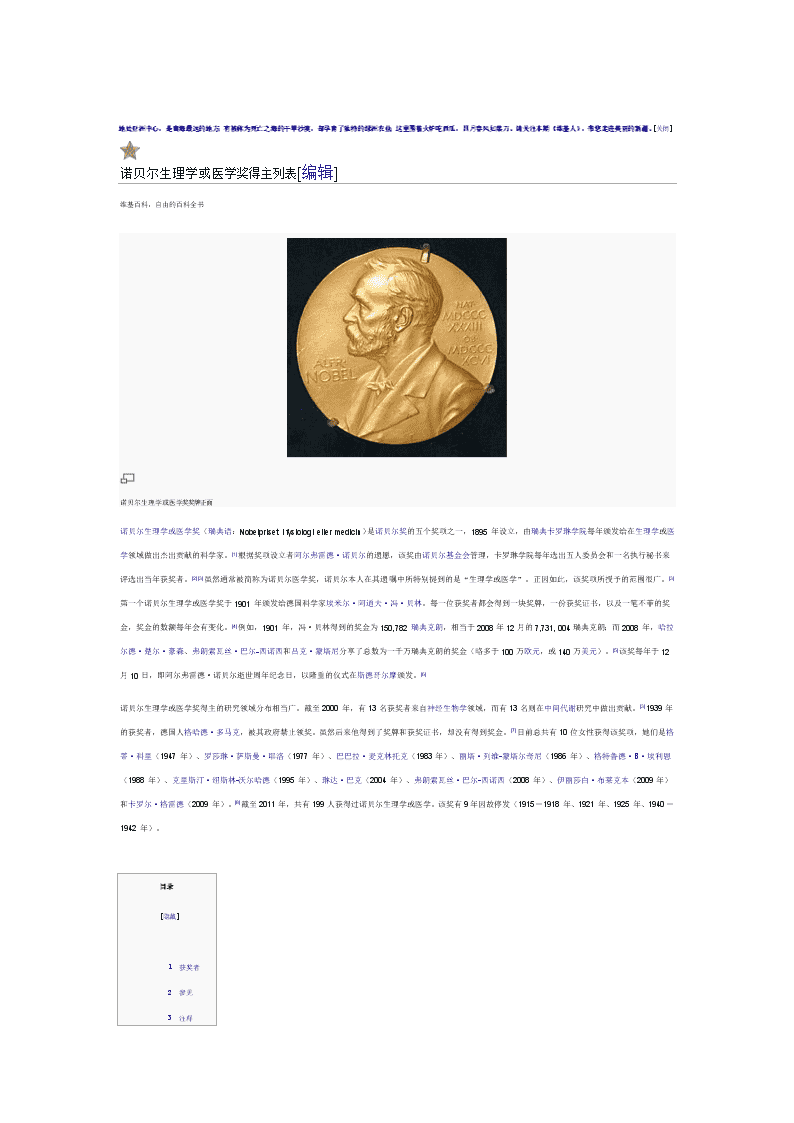
地处亚洲中心,是离海最远的地方;有被称为死亡之海的干旱沙漠,却孕育了独特的绿洲农业;这里围着火炉吃西瓜,四月春风如菜刀。请关注本期《维基人》,带您走进美丽的新疆。[关闭]诺贝尔生理学或医学奖得主列表[编辑]维基百科,自由的百科全书诺贝尔生理学或医学奖奖牌正面诺贝尔生理学或医学奖(瑞典语:Nobelprisetifysiologiellermedicin)是诺贝尔奖的五个奖项之一,1895年设立,由瑞典卡罗琳学院每年颁发给在生理学或医学领域做出杰出贡献的科学家。[1]根据奖项设立者阿尔弗雷德·诺贝尔的遗愿,该奖由诺贝尔基金会管理,卡罗琳学院每年选出五人委员会和一名执行秘书来评选出当年获奖者。[2][3]虽然通常被简称为诺贝尔医学奖,诺贝尔本人在其遗嘱中所特别提到的是“生理学或医学”。正因如此,该奖项所授予的范围很广。[3]第一个诺贝尔生理学或医学奖于1901年颁发给德国科学家埃米尔·阿道夫·冯·贝林。每一位获奖者都会得到一块奖牌,一份获奖证书,以及一笔不菲的奖金,奖金的数额每年会有变化。[4]例如,1901年,冯·贝林得到的奖金为150,782瑞典克朗,相当于2008年12月的7,731,004瑞典克朗;而2008年,哈拉尔德·楚尔·豪森、弗朗索瓦丝·巴尔-西诺西和吕克·蒙塔尼分享了总数为一千万瑞典克朗的奖金(略多于100万欧元,或140万美元)。[5]该奖每年于12月10日,即阿尔弗雷德·诺贝尔逝世周年纪念日,以隆重的仪式在斯德哥尔摩颁发。[6]诺贝尔生理学或医学奖得主的研究领域分布相当广。截至2000年,有13名获奖者来自神经生物学领域,而有13名则在中间代谢研究中做出贡献。[3]1939年的获奖者,德国人格哈德·多马克,被其政府禁止领奖。虽然后来他得到了奖牌和获奖证书,却没有得到奖金。[7]目前总共有10位女性获得该奖项,她们是格蒂·科里(1947年)、罗莎琳·萨斯曼·耶洛(1977年)、巴巴拉·麦克林托克(1983年)、丽塔·列维-蒙塔尔奇尼(1986年)、格特鲁德·B·埃利恩(1988年)、克里斯汀·纽斯林-沃尔哈德(1995年)、琳达·巴克(2004年)、弗朗索瓦丝·巴尔-西诺西(2008年)、伊丽莎白·布莱克本(2009年)和卡罗尔·格雷德(2009年)。[8]截至2011年,共有199人获得过诺贝尔生理学或医学。该奖有9年因故停发(1915-1918年、1921年、1925年、1940-1942年)。目录 [隐藏] ·1 获奖者·2 参见·3 注释
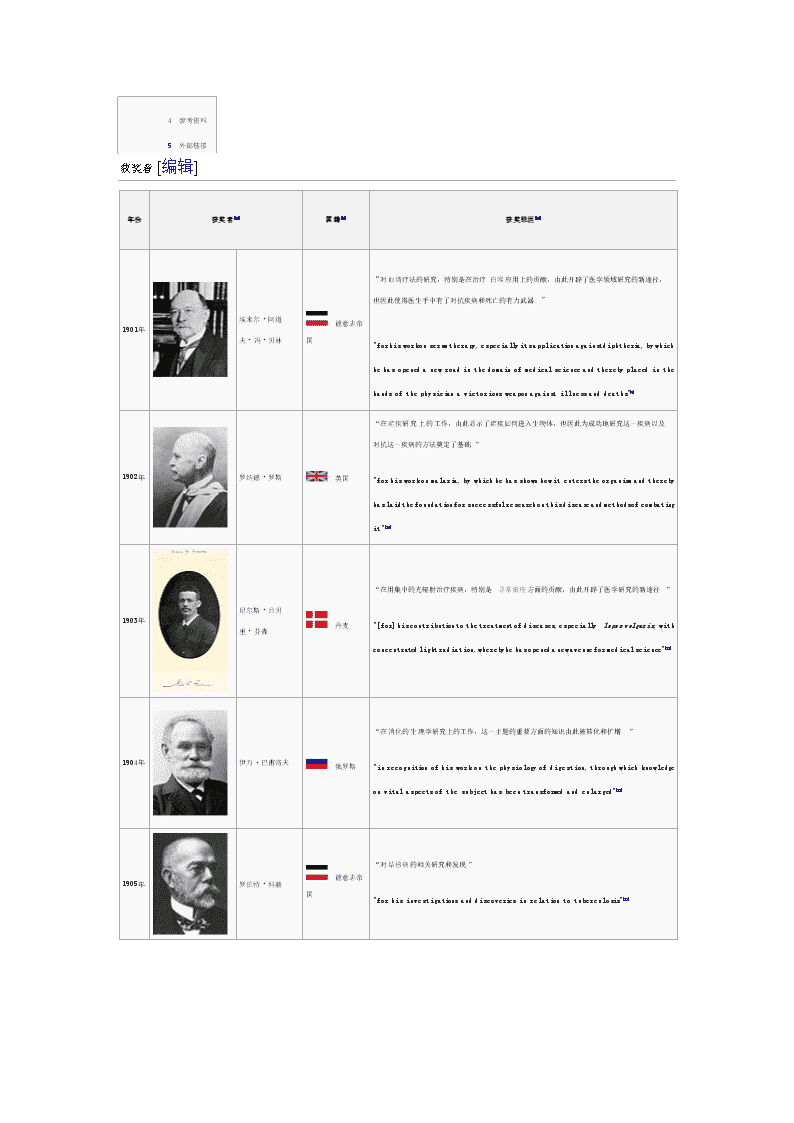
·4 参考资料·5 外部链接获奖者 [编辑]年份获奖者[A]国籍[B]获奖原因[C]1901年埃米尔·阿道夫·冯·贝林 德意志帝国“对血清疗法的研究,特别是在治疗白喉应用上的贡献,由此开辟了医学领域研究的新途径,也因此使得医生手中有了对抗疾病和死亡的有力武器”"forhisworkonserumtherapy,especiallyitsapplicationagainstdiphtheria,bywhichhehasopenedanewroadinthedomainofmedicalscienceandtherebyplacedinthehandsofthephysicianavictoriousweaponagainstillnessanddeaths"[9]1902年罗纳德·罗斯 英国“在疟疾研究上的工作,由此显示了疟疾如何进入生物体,也因此为成功地研究这一疾病以及对抗这一疾病的方法奠定了基础”"forhisworkonmalaria,bywhichhehasshownhowitenterstheorganismandtherebyhaslaidthefoundationforsuccessfulresearchonthisdiseaseandmethodsofcombatingit"[10]1903年尼尔斯·吕贝里·芬森 丹麦“在用集中的光辐射治疗疾病,特别是寻常狼疮方面的贡献,由此开辟了医学研究的新途径”"[for]hiscontributiontothetreatmentofdiseases,especially lupusvulgaris,withconcentratedlightradiation,wherebyhehasopenedanewavenueformedicalscience"[11]1904年伊万·巴甫洛夫 俄罗斯“在消化的生理学研究上的工作,这一主题的重要方面的知识由此被转化和扩增”"inrecognitionofhisworkonthephysiologyofdigestion,throughwhichknowledgeonvitalaspectsofthesubjecthasbeentransformedandenlarged"[12]1905年罗伯特·科赫 德意志帝国“对结核病的相关研究和发现”"forhisinvestigationsanddiscoveriesinrelationtotuberculosis"[13]
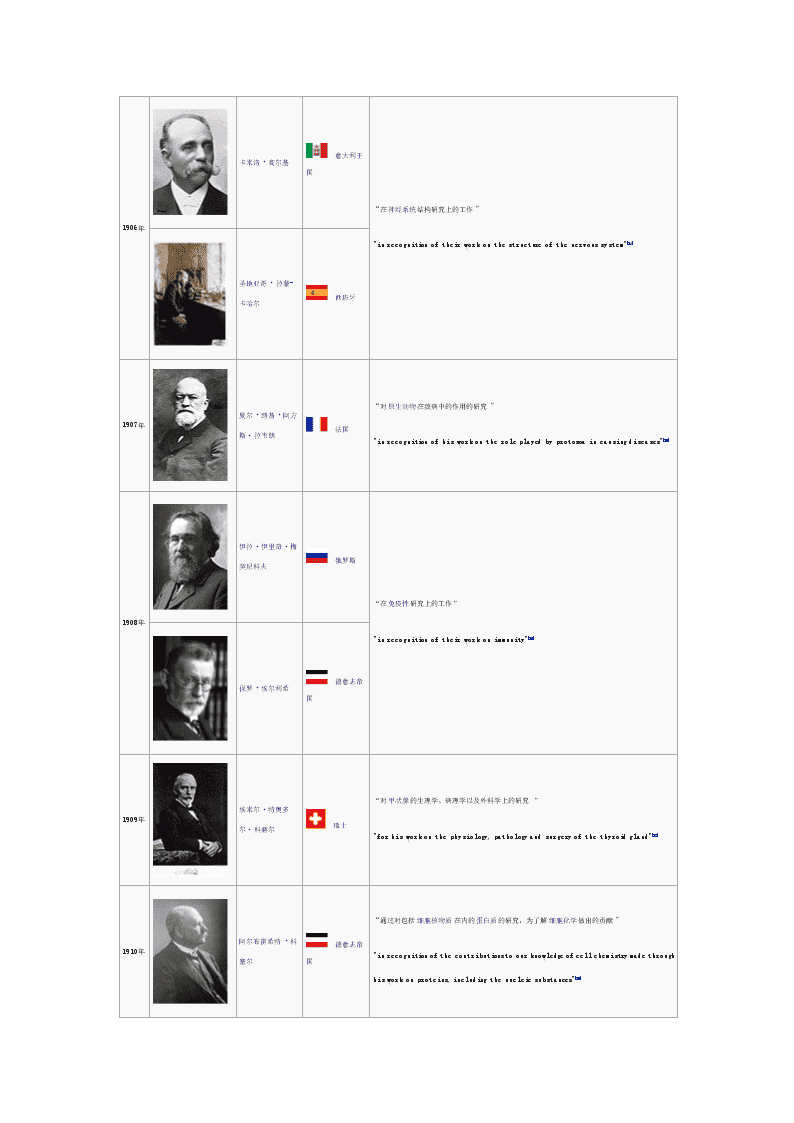
1906年卡米洛·高尔基 意大利王国“在神经系统结构研究上的工作”"inrecognitionoftheirworkonthestructureofthenervoussystem"[14]圣地亚哥·拉蒙-卡哈尔 西班牙1907年夏尔·路易·阿方斯·拉韦朗 法国“对原生动物在致病中的作用的研究”"inrecognitionofhisworkontheroleplayedbyprotozoaincausingdiseases"[15]1908年伊拉·伊里奇·梅契尼科夫 俄罗斯“在免疫性研究上的工作”"inrecognitionoftheirworkonimmunity"[16]保罗·埃尔利希 德意志帝国1909年埃米尔·特奥多尔·科赫尔 瑞士“对甲状腺的生理学、病理学以及外科学上的研究”"forhisworkonthephysiology,pathologyandsurgeryofthethyroidgland"[17]1910年阿尔布雷希特·科塞尔 德意志帝国“通过对包括细胞核物质在内的蛋白质的研究,为了解细胞化学做出的贡献”"inrecognitionofthecontributionstoourknowledgeofcellchemistrymadethroughhisworkonproteins,includingthenucleicsubstances"[18]
1911年阿尔瓦·古尔斯特兰德 瑞典“在眼睛屈光学研究上的工作”"forhisworkonthedioptricsoftheeye"[19]1912年亚历克西·卡雷尔 法国“在血管结构以及血管和器官移植研究上的工作”"[for]hisworkonvascularsutureandthetransplantationofbloodvesselsandorgans"[20]1913年夏尔·罗贝尔·里歇 法国“在过敏反应研究上的工作”"[for]hisworkonanaphylaxis"[21]1914年罗伯特·巴拉尼 奥地利“在前庭器官的生理学与病理学研究上的工作”"forhisworkonthephysiologyandpathologyofthevestibularapparatus"[22]1915年未颁奖1916年1917年1918年1919年朱尔·博尔代 比利时“免疫性方面的发现”"forhisdiscoveriesrelatingtoimmunity"[23]1920年奥古斯特·克罗 丹麦“发现毛细血管运动的调节机理”"forhisdiscoveryofthecapillarymotorregulatingmechanism"[24]1921年未颁奖
1922年阿奇博尔德·希尔 英国“在肌肉产生热量上的发现”"forhisdiscoveryrelatingtotheproductionofheatinthemuscle"[25]奥托·迈尔霍夫 德国“发现肌肉中氧的消耗和乳酸代谢之间的固定关系”"forhisdiscoveryofthefixedrelationshipbetweentheconsumptionofoxygenandthemetabolismoflacticacidinthemuscle"[25]1923年弗雷德里克·格兰特·班廷 加拿大“发现胰岛素”"forthediscoveryofinsulin"[26]约翰·麦克劳德 加拿大1924年威廉·埃因托芬 荷兰“发明心电图装置”"forthediscoveryofthemechanismoftheelectrocardiogram"[27]1925年未颁奖1926年约翰尼斯·菲比格 丹麦“发现鼠癌”"forhisdiscoveryofthe Spiropteracarcinoma"[28]1927年朱利叶斯·瓦格纳-尧雷格 奥地利“发现在治疗麻痹性痴呆过程中疟疾接种疗法的治疗价值”"forhisdiscoveryofthetherapeuticvalueofmalariainoculationinthetreatmentofdementiaparalytica"[29]
1928年查尔斯·尼柯尔 法国“在斑疹伤寒研究上的工作”"forhisworkontyphus"[30]1929年克里斯蒂安·艾克曼 荷兰“发现抗神经炎的维生素”"forhisdiscoveryoftheantineuriticvitamin"[31]弗雷德里克·霍普金斯爵士 英国“发现刺激生长的维生素”"forhisdiscoveryofthegrowth-stimulatingvitamin"[31]1930年卡尔·兰德施泰纳 奥地利“发现人类的血型”"forhisdiscoveryofhumanbloodgroups"[32]1931年奥托·海因里希·瓦尔堡 德国“发现呼吸酶的性质和作用方式”"forhisdiscoveryofthenatureandmodeofactionoftherespiratoryenzyme"[33]1932年查尔斯·斯科特·谢灵顿爵士 英国“发现神经元的相关功能”"fortheirdiscoveriesregardingthefunctionsofneurons"[34]埃德加·阿德里安 英国
1933年托马斯·亨特·摩尔根 美国“发现遗传中染色体所起的作用”"forhisdiscoveriesconcerningtheroleplayedbythechromosomeinheredity"[35]1934年乔治·惠普尔 美国“发现贫血的肝脏治疗法”"fortheirdiscoveriesconcerninglivertherapyincasesofanaemia"[36]乔治·迈诺特 美国威廉·莫菲 美国1935年汉斯·斯佩曼 德国“发现胚胎发育中的组织者(胚胎发育中起中心作用的胚胎区域)效应”"forhisdiscoveryoftheorganizereffectinembryonicdevelopment"[37]1936年亨利·哈利特·戴尔爵士 英国“神经冲动的化学传递的相关发现”"fortheirdiscoveriesrelatingtochemicaltransmissionofnerveimpulses"[38]奥托·勒维 奥地利
1937年圣捷尔吉·阿尔伯特 匈牙利“与生物燃烧过程有关的发现,特别是关于维生素C和延胡索酸的催化作用”"forhisdiscoveriesinconnectionwiththebiologicalcombustionprocesses,withspecialreferencetovitaminCandthecatalysisoffumaricacid"[39]1938年海门斯 比利时“发现窦和主动脉机制在呼吸调节中所起的作用”"forthediscoveryoftheroleplayedbythesinusandaorticmechanismsintheregulationofrespiration"[40]1939年格哈德·多马克 德国“发现百浪多息(一种磺胺类药物)的抗菌效果”"forthediscoveryoftheantibacterialeffectsofprontosil"[41]1940年未颁奖1941年1942年1943年亨利克·达姆 丹麦“发现维生素K”"forhisdiscoveryofvitaminK"[42]爱德华·阿德尔伯特·多伊西 美国“发现维生素K的化学性质”"forhisdiscoveryofthechemicalnatureofvitaminK"[42]1944年约瑟夫·厄尔兰格 美国“发现单神经纤维的高度分化功能”"fortheirdiscoveriesrelatingtothehighlydifferentiatedfunctionsofsinglenervefibres"[43]
赫伯特·斯潘塞·加塞 美国1945年亚历山大·弗莱明爵士 英国“发现青霉素及其对各种传染病的疗效”"forthediscoveryofpenicillinanditscurativeeffectinvariousinfectiousdiseases"[44]恩斯特·伯利斯·柴恩 英国霍华德·弗洛里爵士 澳大利亚1946年75px赫尔曼·约瑟夫·马勒 美国“发现用X射线辐射的方法能够产生突变”"forthediscoveryoftheproductionofmutationsbymeansofX-rayirradiation"[45]1947年卡尔·斐迪南·科里 美国“发现糖原的催化转化原因”"fortheirdiscoveryofthecourseofthecatalyticconversionofglycogen"[46]格蒂·特蕾莎·科里 美国贝尔纳多·奥赛 阿根廷“发现垂体前叶激素在糖代谢中的作用”"forhisdiscoveryofthepartplayedbythehormoneoftheanteriorpituitarylobeinthemetabolismofsugar"[46]
1948年保罗·赫尔曼·穆勒 瑞士“发现DDT是一种高效杀死多类节肢动物的接触性毒药”"forhisdiscoveryofthehighefficiencyofDDTasacontactpoisonagainstseveralarthropods"[47]1949年瓦尔特·鲁道夫·赫斯 瑞士“发现间脑的功能性组织对内脏活动的调节功能”"forhisdiscoveryofthefunctionalorganizationoftheinterbrainasacoordinatoroftheactivitiesoftheinternalorgans"[48]安东尼奥·埃加斯·莫尼斯 葡萄牙“发现前脑叶白质切除术对特定重性精神病患者的治疗效果”"forhisdiscoveryofthetherapeuticvalueofleucotomyincertainpsychoses"[48]1950年75px菲利普·肖瓦特·亨奇 美国“发现肾上腺皮质激素及其结构和生物效应”"fortheirdiscoveriesrelatingtothehormonesoftheadrenalcortex,theirstructureandbiologicaleffects"[49]75px爱德华·卡尔文·肯德尔 美国塔德乌什·赖希施泰因 瑞士1951年马克斯·泰累尔 南非“黄热病及其治疗方法上的发现”"forhisdiscoveriesconcerningyellowfeverandhowtocombatit"[50]1952年赛尔曼·A·瓦克斯曼 美国“发现链霉素,第一个有效对抗结核病的抗生素”"forhisdiscoveryofstreptomycin,thefirstantibioticeffectiveagainsttuberculosis"[51]
1953年汉斯·阿道夫·克雷布斯 英国“发现柠檬酸循环”"forhisdiscoveryofthecitricacidcycle"[52]弗里茨·阿尔贝特·李普曼 美国“发现辅酶A及其对中间代谢的重要性”"forhisdiscoveryofco-enzymeAanditsimportanceforintermediarymetabolism"[52]1954年约翰·富兰克林·恩德斯 美国“发现脊髓灰质炎病毒在各种组织培养基中的生长能力”"fortheirdiscoveryoftheabilityofpoliomyelitisvirusestogrowinculturesofvarioustypesoftissue"[53]75px弗雷德里克·查普曼·罗宾斯 美国75px托马斯·哈克尔·韦勒 美国1955年阿克塞尔·胡戈·特奥多尔·特奥雷尔 瑞典“发现氧化酶的性质和作用方式”"forhisdiscoveriesconcerningthenatureandmodeofactionofoxidationenzymes"[54]1956年75px安德烈·弗雷德里克·考南德 美国“心脏导管术及其在循环系统的病理变化方面的发现”"fortheirdiscoveriesconcerningheartcatheterizationandpathologicalchangesinthecirculatorysystem"[55]沃纳·福斯曼 德国75px迪金森·伍德拉夫·理查兹 美国1957年达尼埃尔·博韦 意大利“发现抑制某些机体物质作用的合成化合物,特别是对血管系统和骨骼肌的作用”"forhisdiscoveriesrelatingtosyntheticcompoundsthatinhibittheactionofcertainbodysubstances,andespeciallytheiractiononthevascularsystemandtheskeletalmuscles"[56]1958年75px乔治·韦尔斯·比德尔 美国“发现基因功能受到特定化学过程的调控”
"fortheirdiscoverythatgenesactbyregulatingdefinitechemicalevents"[57]75px爱德华·劳里·塔特姆 美国75px乔舒亚·莱德伯格 美国“发现细菌遗传物质的基因重组和组织”"forhisdiscoveriesconcerninggeneticrecombinationandtheorganizationofthegeneticmaterialofbacteria"[57]1959年阿瑟·科恩伯格 美国“发现核糖核酸和脱氧核糖核酸的生物合成机制”"fortheirdiscoveryofthemechanismsinthebiologicalsynthesisofribonucleicacidanddeoxyribonucleicacid"[58]塞韦罗·奥乔亚 美国1960年弗兰克·麦克法兰·伯内特爵士 澳大利亚“发现获得性免疫耐受”"fordiscoveryofacquiredimmunologicaltolerance"[59]彼得·梅达沃 英国1961年盖欧尔格·冯·贝凯希 美国“发现耳蜗内刺激的物理机理”"forhisdiscoveriesofthephysicalmechanismofstimulationwithinthecochlea"[60]1962年佛朗西斯·克里克 英国“发现核酸的分子结构及其对生物中信息传递的重要性”"fortheirdiscoveriesconcerningthemolecularstructureofnucleicacidsandits
significanceforinformationtransferinlivingmaterial"[61]詹姆斯·杜威·沃森 美国莫里斯·威尔金斯 新西兰 英国1963年约翰·卡鲁·埃克尔斯爵士 澳大利亚“发现在神经细胞膜的外围和中心部位与神经兴奋和抑制有关的离子机理”"fortheirdiscoveriesconcerningtheionicmechanismsinvolvedinexcitationandinhibitionintheperipheralandcentralportionsofthenervecellmembrane"[62]艾伦·劳埃德·霍奇金 英国安德鲁·赫胥黎 英国1964年康拉德·布洛赫 美国“发现胆固醇和脂肪酸的代谢机理和调控作用”"fortheirdiscoveriesconcerningthemechanismandregulationofthecholesterolandfattyacidmetabolism"[63]费奥多尔·吕嫩 德国1965年方斯华·贾克柏 法国“在酶和病毒合成的遗传控制中的发现”
"fortheirdiscoveriesconcerninggeneticcontrolofenzymeandvirussynthesis"[64]安德列·利沃夫 法国贾克·莫诺 法国1966年裴顿·劳斯 美国“发现诱导肿瘤的病毒”"forhisdiscoveryoftumour-inducingviruses"[65]查尔斯·布兰顿·哈金斯 美国“发现前列腺癌的激素疗法”"forhisdiscoveriesconcerninghormonaltreatmentofprostaticcancer"[65]1967年拉格纳·格拉尼特 瑞典“发现眼睛的初级生理及化学视觉过程”"fortheirdiscoveriesconcerningtheprimaryphysiologicalandchemicalvisualprocessesintheeye"[66]霍尔登·凯弗·哈特兰 美国乔治·沃尔德 美国1968年罗伯特·W·霍利 美国“破解遗传密码并阐释其在蛋白质合成中的作用”"fortheirinterpretationofthegeneticcodeanditsfunctioninproteinsynthesis"[67]哈尔·葛宾·科拉纳 美国马歇尔·沃伦·尼伦伯格 美国1969年马克斯·德尔布吕克 美国“发现病毒的复制机理和遗传结构”"fortheirdiscoveriesconcerningthereplicationmechanismandthegeneticstructureofviruses"[68]
阿弗雷德·赫希 美国萨尔瓦多·卢瑞亚 美国1970年朱利叶斯·阿克塞尔罗德 美国“发现神经末梢中的体液性传递物质及其贮存、释放和抑制机理”"fortheirdiscoveriesconcerningthehumoraltransmittorsinthenerveterminalsandthemechanismfortheirstorage,releaseandinactivation"[69]乌尔夫·冯·奥伊勒 瑞典伯纳德·卡茨爵士 英国1971年埃鲁·威尔布尔·苏德兰 美国“发现激素的作用机理”"forhisdiscoveriesconcerningthemechanismsoftheactionofhormones"[70]1972年杰拉尔德·埃德尔曼 美国“发现抗体的化学结构”"fortheirdiscoveriesconcerningthechemicalstructureofantibodies"[71]罗德尼·罗伯特·波特 英国1973年卡尔·冯·弗利 德国“发现个体与社会性行为模式的组织和引发”"fortheirdiscoveriesconcerningorganizationandelicitationofindividualandsocialbehaviourpatterns"[72]康拉德·洛伦兹 奥地利尼可拉斯·庭伯根 英国1974年阿尔伯特·克劳德 比利时“细胞的结构和功能组织方面的发现”"fortheirdiscoveriesconcerningthestructuralandfunctionalorganizationofthecell"[73]克里斯汀·德·迪夫 比利时乔治·埃米尔·帕拉德 美国1975年戴维·巴尔的摩 美国“发现肿瘤病毒和细胞的遗传物质之间的相互作用”"fortheirdiscoveriesconcerningtheinteractionbetweentumorvirusesandthegeneticmaterialofthecell"[74]罗纳托·杜尔贝科 美国霍华德·马丁·特明 美国
1976年巴鲁克·塞缪尔·布隆伯格 美国“发现传染病产生和传播的新机理”"fortheirdiscoveriesconcerningnewmechanismsfortheoriginanddisseminationofinfectiousdiseases"[75]丹尼尔·卡尔顿·盖杜谢克 美国1977年罗歇·吉耶曼 美国“发现大脑分泌的肽类激素”"fortheirdiscoveriesconcerningthepeptidehormoneproductionofthebrain"[76]安德鲁·沙利 美国罗莎琳·萨斯曼·耶洛 美国“开发肽类激素的放射免疫分析法”"forthedevelopmentofradioimmunoassaysofpeptidehormones"[76]1978年沃纳·亚伯 瑞士“发现限制性内切酶及其在分子遗传学方面的应用”"forthediscoveryofrestrictionenzymesandtheirapplicationtoproblemsofmoleculargenetics"[77]丹尼尔·那森斯 美国汉弥尔顿·史密斯 美国1979年阿兰·麦克莱德·科马克 美国“开发计算机辅助的断层扫描技术”"forthedevelopmentofcomputerassistedtomography"[78]高弗雷·豪斯费尔德 英国1980年巴茹·贝纳塞拉夫 美国“发现调节免疫反应的细胞表面受体的遗传结构”"fortheirdiscoveriesconcerninggeneticallydeterminedstructuresonthecellsurfacethatregulateimmunologicalreactions"[79]让·多塞 法国乔治·斯内尔 美国1981年罗杰·斯佩里 美国“发现大脑半球的功能性分工”"forhisdiscoveriesconcerningthefunctionalspecializationofthecerebralhemispheres"[80]大卫·休伯尔 美国“发现视觉系统的信息加工”
"fortheirdiscoveriesconcerninginformationprocessinginthevisualsystem"[80]托斯坦·维厄瑟尔 瑞典1982年苏恩·伯格斯特龙 瑞典“发现前列腺素及其相关的生物活性物质”"fortheirdiscoveriesconcerningprostaglandinsandrelatedbiologicallyactivesubstances"[81]本格特·萨米尔松 瑞典约翰·范恩 英国1983年75px巴巴拉·麦克林托克 美国“发现可移动的遗传元素”"forherdiscoveryofmobilegeneticelements"[82]1984年尼尔斯·杰尼 丹麦“关于免疫系统的发育和控制特异性的理论,以及发现单克隆抗体产生的原理”"fortheoriesconcerningthespecificityindevelopmentandcontroloftheimmunesystemandthediscoveryoftheprincipleforproductionofmonoclonalantibodies"[83]乔治斯·克勒 德国色萨·米尔斯坦 阿根廷 英国1985年麦可·布朗 美国“在胆固醇代谢的调控方面的发现”"fortheirdiscoveriesconcerningtheregulationofcholesterolmetabolism"[84]约瑟夫·里欧纳德·戈尔茨坦 美国1986年斯坦利·科恩 美国“发现生长因子”"fortheirdiscoveriesofgrowthfactors"[85]丽塔·列维-蒙塔尔奇尼 意大利 美国
1987年利根川进 日本“发现抗体多样性产生的遗传学原理”"forhisdiscoveryofthegeneticprincipleforgenerationofantibodydiversity"[86]1988年詹姆士·W·布拉克爵士 英国“发现药物治疗的重要原理”"fortheirdiscoveriesofimportantprinciplesfordrugtreatment"[87]格特鲁德·B·埃利恩 美国乔治·希青斯 美国1989年迈克尔·毕晓普 美国“发现逆转录病毒致癌基因的细胞来源”"fortheirdiscoveryofthecellularoriginofretroviraloncogenes"[88]哈罗德·瓦慕斯 美国1990年约瑟夫·默里 美国“发明应用于人类疾病治疗的器官和细胞移植术”"fortheirdiscoveriesconcerningorganandcelltransplantationinthetreatmentofhumandisease"[89]唐纳尔·托马斯 美国1991年厄温·内尔 德国“发现细胞中单离子通道的功能”"fortheirdiscoveriesconcerningthefunctionofsingleionchannelsincells"[90]伯特·萨克曼 德国1992年埃德蒙·费希尔 瑞士 美国“发现的可逆的蛋白质磷酸化作用是一种生物调节机制”"fortheirdiscoveriesconcerningreversibleproteinphosphorylationasabiologicalregulatorymechanism"[91]埃德温·克雷布斯 美国
1993年理察·罗伯茨 英国“发现断裂基因”"fortheirdiscoveriesofsplitgenes"[92]菲利普·夏普 美国1994年艾尔佛列·古曼·吉尔曼 美国“发现G蛋白及其在细胞中的信号转导作用”"fortheirdiscoveryofG-proteinsandtheroleoftheseproteinsinsignaltransductionincells"[93]马丁·罗德贝尔 美国1995年爱德华·路易斯 美国“发现早期胚胎发育中的遗传调控机理”"fortheirdiscoveriesconcerningthegeneticcontrolofearlyembryonicdevelopment"[94]克里斯汀·纽斯林-沃尔哈德 德国艾瑞克·威斯乔斯 美国1996年彼得·杜赫提 澳大利亚“发现细胞介导的免疫防御特性”"fortheirdiscoveriesconcerningthespecificityofthecellmediatedimmunedefence"[95]罗夫·辛克纳吉 瑞士1997年史坦利·布鲁希纳 美国“发现朊病毒——传染的一种新的生物学原理”"forhisdiscoveryofPrions-anewbiologicalprincipleofinfection"[96]1998年罗伯·佛契哥特 美国“发现在心血管系统中起信号分子作用的一氧化氮”"fortheirdiscoveriesconcerningnitricoxideasasignallingmoleculeinthecardiovascularsystem"[97]路易斯·路伊格纳洛 美国
费瑞·慕拉德 美国1999年古特·布洛伯尔 美国“发现蛋白质具有内在信号以控制其在细胞内的传递和定位”"forthediscoverythatproteinshaveintrinsicsignalsthatgoverntheirtransportandlocalizationinthecell"[98]2000年阿尔维德·卡尔森 瑞典“发现神经系统中的信号传导”"fortheirdiscoveriesconcerningsignaltransductioninthenervoussystem"[99]保罗·格林加德 美国艾瑞克·坎德尔 美国2001年利兰·哈特韦尔 美国“发现细胞周期的关键调节因子”"fortheirdiscoveriesofkeyregulatorsofthecellcycle"[100]蒂姆·亨特 英国保罗·纳斯爵士 英国2002年悉尼·布伦纳 英国“发现器官发育和细胞程序性死亡的遗传调控机理”"fortheirdiscoveriesconcerning"geneticregulationoforgandevelopmentandprogrammedcelldeath""[101]H·罗伯特·霍维茨 美国约翰·E·苏尔斯顿 美国
2003年保罗·劳特伯 美国“在核磁共振成像方面的发现”"fortheirdiscoveriesconcerningmagneticresonanceimaging"[102]彼得·曼斯菲尔德爵士 英国2004年理查德·阿克塞尔 美国“发现嗅觉受体和嗅觉系统的组织方式”"fortheirdiscoveriesofodorantreceptorsandtheorganizationoftheolfactorysystem"[103]琳达·巴克 美国2005年巴里·马歇尔 澳大利亚“发现幽门螺杆菌及其在胃炎和胃溃疡中所起的作用”"fortheirdiscoveryofthebacterium Helicobacterpylori anditsroleingastritisandpepticulcerdisease"[104]罗宾·沃伦 澳大利亚2006年安德鲁·法厄 美国“发现了RNA干扰——双链RNA引发的沉默现象”"fortheirdiscoveryofRNAinterference-genesilencingbydouble-strandedRNA"[105]克雷格·梅洛 美国2007年马里奥·卡佩奇 美国“在利用胚胎干细胞引入特异性基因修饰的原理上的发现”"fortheirdiscoveriesofprinciplesforintroducingspecificgenemodificationsinmicebytheuseofembryonicstemcells."[106]
马丁·埃文斯爵士 英国奥利弗·史密斯 美国2008年哈拉尔德·楚尔·豪森 德国“发现了导致子宫颈癌的人乳头状瘤病毒”"forhisdiscoveryofhumanpapillomavirusescausingcervicalcancer"[107]弗朗索瓦丝·巴尔-西诺西 法国“发现人类免疫缺陷病毒(即艾滋病病毒)”"fortheirdiscoveryofhumanimmunodeficiencyvirus"[107]吕克·蒙塔尼 法国2009年伊丽莎白·布莱克本 美国 澳大利亚“发现端粒和端粒酶如何保护染色体”"forthediscoveryofhowchromosomesareprotectedbytelomeresandtheenzymetelomerase"[108]卡罗尔·格雷德 美国
杰克·绍斯塔克 美国 英国2010年罗伯特·杰弗里·爱德华兹 英国“因为在试管婴儿方面的研究获奖”"forthedevelopmentofinvitrofertilization"[109]2011年博伊特勒 美国"他们对于先天免疫机制激活的发现""fortheirdiscoveriesconcerningtheactivationofinnateimmunity"[110]奥夫曼 法国斯坦曼 加拿大 美国"他发现树突状细胞和其在后天免疫中的作用""forhisdiscoveryofthedendriticcellanditsroleinadaptiveimmunity"[110] (awardedposthumously)[111]2012年约翰·格登爵士 英国“发现成熟细胞可被重写成多功能细胞”"forthediscoverythatmaturecellscanbereprogrammedtobecomepluripotent"[112]山中伸弥 日本参见 [编辑]·各国诺贝尔奖得主列表注释 [编辑]^ A.这里的中文姓名是根据诺贝尔基金会的官方主页(nobelprize.org)提供英文名字的翻译,对于得奖者的原名或其他名字,可从该得奖者的条目中了解。华人或日本人姓名按中文和日文姓名习惯翻译。尽可能提供了每一位获奖者的照片;如果需要,可以到诺贝尔基金会的官方主页上查询每一位获奖者的照片。^ B.这里的国家信息是根据诺贝尔基金会的官方主页提供的信息列出,并不一定为得奖者真实的国籍或出生地。
^ C.这里所引用的获奖理由是根据诺贝尔基金会的官方主页提供的英文原文翻译列出,英文原文被列于中文翻译之后以供查对。这一栏中的条目链接是与获奖者的获奖原因相关的研究领域与历史;这些链接这是作为指引和解释,需要了解每一位获奖者的具体工作,请由名字一栏中的链接到对应得奖者的条目中查看,或到诺贝尔基金会的官方主页中相关获奖者的页面中查看。参考资料 [编辑]一般·(英文)所有诺贝尔生理学或医学奖获得者. 诺贝尔基金会(NobelFoundation). [2008-10-06].·(英文)诺贝尔奖获得者. 大英百科全书. [2008-10-15].特殊1.^ AlfredNobel–TheManBehindtheNobelPrize.NobelFoundation. [2008-11-21].2.^ TheNobelPrizeAwarders.NobelFoundation. [2008-11-21].3.^ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Lindsten,JanandNilsRingertz.TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine,1901–2000*.NobelFoundation.2001-06-26[2008-11-21].4.^ TheNobelPrize.NobelFoundation. [2008-11-21].5.^ TheNobelPrizeAmounts.NobelFoundation.[2008-11-21].6.^ TheNobelPrizeAwardCeremonies.NobelFoundation. [2008-11-21].7.^ NobelLaureatesFacts.Nobelprize.org.[2008-11-21].8.^ WomenNobelLaureates.NobelFoundation.[2008-11-21].9.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1901.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].10.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1902.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].11.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1903.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].12.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1904.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].13.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1905.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].14.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1906.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].15.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1907.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].16.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1908.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].17.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1909.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].18.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1910.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].19.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1911.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].20.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1912.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].21.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1913.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].22.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1914.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].23.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1919.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].24.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1920.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].25.^ 25.0 25.1 TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1922.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].
1.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1923.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].2.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1924.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].3.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1926.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].4.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1927.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].5.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1928.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].6.^ 31.0 31.1 TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1929.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].7.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1930.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].8.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1931.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].9.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1932.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].10.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1933.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].11.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1934.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].12.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1935.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].13.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1936.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].14.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1937.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].15.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1938.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].16.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1939.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].17.^ 42.0 42.1 TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1943.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].18.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1944.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].19.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1945.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].20.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1946.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].21.^ 46.0 46.1 TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1947.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].22.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1948.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].23.^ 48.0 48.1 TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1949.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].24.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1950.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].25.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1951.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].26.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1952.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].27.^ 52.0 52.1 TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1953.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].28.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1954.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].29.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1955.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].30.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1956.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].31.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1957.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].32.^ 57.0 57.1 TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1958.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].33.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1959.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].34.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1960.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].35.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1961.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].36.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1962.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].
1.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1963.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].2.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1964.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].3.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1965.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].4.^ 65.0 65.1 TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1966.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].5.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1967.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].6.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1968.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].7.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1969.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].8.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1970.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].9.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1971.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].10.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1972.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].11.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1973.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].12.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1974.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].13.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1975.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].14.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1976.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].15.^ 76.0 76.1 TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1977.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].16.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1978.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].17.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1979.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].18.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1980.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].19.^ 80.0 80.1 TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1981.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].20.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1982.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].21.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1983.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].22.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1984.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].23.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1985.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].24.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1986.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].25.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1987.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].26.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1988.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].27.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1989.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].28.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1990.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].29.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1991.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].30.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1992.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].31.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1993.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].32.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1994.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].33.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1995.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].34.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1996.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].35.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1997.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].36.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1998.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].
1.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine1999.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].2.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine2000.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].3.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine2001.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].4.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine2002.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].5.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine2003.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].6.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine2004.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].7.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine2005.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].8.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine2006.NobelFoundation. [2007-07-28].9.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine2007.NobelFoundation. [2007-10-08].10.^ 107.0 107.1 TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine2008.NobelFoundation. [2008-10-06].11.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine2009.NobelFoundation. [2009-10-06].12.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine2010.NobelFoundation. [2010-10-04].13.^ 110.0 110.1 TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine2011.NobelFoundation. [2011-10-03].14.^ RalphSteinmanRemainsNobelLaureate. TheNobelFoundation.3October2011 [4October2011].15.^ TheNobelPrizeinPhysiologyorMedicine2012.NobelFoundation. [2012-10-08].
您可能关注的文档
- 内蒙古呼伦贝尔市2018届九年级物理上学期第一次月考试题新人教版
- 诺贝尔经济学奖获得者
- 五年级语文上册21诺贝尔教案苏教版.doc
- 五年级语文上册21诺贝尔教案苏教版2.doc
- 暑假呼伦贝尔亲子游
- 莫言诺贝尔文学奖演讲发言稿《讲故事的人》修订校正版
- 2000-2012年诺贝尔经济学奖的相关信息
- [管理]2013呼伦贝尔半自助旅行攻略 高清多图
- 诺贝尔物理学奖百年回眸【共享精品.doc】
- 呼伦贝尔市财政局国库科2014年2月8日印发
- 呼伦贝尔市海拉尔区水资源办公室采购通用设备
- 呼伦贝尔合同样本电子版
- 呼伦贝尔市生物中考题纲
- 内蒙古呼伦贝尔市2013年中考语文真题试题
- 光船租赁合同(贝尔康)
- 诺贝尔物理学奖—百年回眸[精彩]
- 公路工程试验检测人员考试题_____呼伦贝尔土工试验检测技术考试答案
- 主题人物阅读——屠呦呦获得诺贝尔医学奖